Current Architecture for Layered Security in Warm Cryptocurrency Wallets
As of October 2025, warm wallets offer a balance between accessibility and security. Explore the multi-layered defense architecture that protects digital assets, from MPC to AI-driven monitoring.
Warm wallets, which offer a balance between the accessibility of hot wallets (always online) and the security of cold wallets (offline), typically incorporate intermittent connectivity for transactions while emphasizing multi-layered security to mitigate risks like phishing, malware, and unauthorized access.
Layered security, or defense-in-depth, involves multiple overlapping protections so that if one layer fails, others remain effective. This architecture has evolved in 2025 with advancements in multi-party computation (MPC), secure enclaves, and AI-driven monitoring, as seen in solutions from providers like Fireblocks and Coincover.
The core architecture often integrates hot and cold elements: small amounts in warm storage for quick access, with bulk assets in cold storage, connected via secure protocols during "warming" processes. Key components include hardware isolation, cryptographic safeguards, and real-time oversight. Below is a summary of the typical layers, drawn from current best practices.
Secure Wallet Architecture Overview
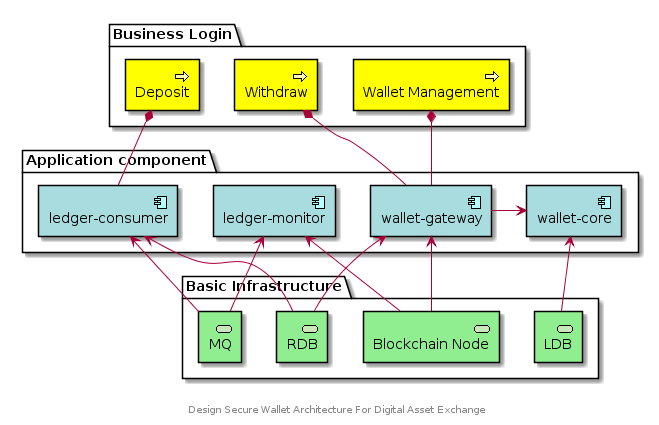
Secure Wallet Architecture Diagram
Visual representation of warm wallet security layers and components
Key Layers in Warm Wallet Security Architecture
Physical/Hardware Layer
Involves offline or semi-offline storage to prevent remote hacks. Warm wallets use hardware security modules (HSMs) or air-gapped devices for key generation and signing, with limited online exposure.
Technologies/Practices:
Hardware wallets (e.g., Ledger, Trezor with warm integrations), secure enclaves (e.g., Intel SGX).
Purpose: Protects against remote exploits; ensures keys are never fully online.
Cryptographic Layer
Employs advanced encryption and key management to secure data and transactions.
Technologies/Practices:
Multi-signature (multi-sig) requiring 2+ approvals, MPC for distributed key handling without full key exposure, end-to-end encryption.
Purpose: Prevents single-point failures; enables secure multi-user access.
Authentication Layer
Verifies user identity and device integrity before allowing access or transactions.
Technologies/Practices:
Multi-factor authentication (MFA/2FA, preferably hardware-based like YubiKey), biometrics, behavioral analysis for anomaly detection.
Purpose: Blocks unauthorized entry; detects phishing or device compromises.
Network/Transaction Layer
Monitors and secures connections and fund movements in real-time.
Technologies/Practices:
VPNs for public Wi-Fi, transaction screening tools (e.g., MistTrack for risk scoring), policy engines to enforce rules like whitelisting addresses.
Purpose: Prevents man-in-the-middle attacks and fraudulent transfers.
Monitoring & Recovery Layer
Provides ongoing surveillance and fallback options for incidents.
Technologies/Practices:
Automated audits, malware detection, encrypted backups, insurance (e.g., via Coincover), revocation tools for compromised sessions.
Purpose: Enables quick response to threats and asset recovery post-breach.
Layer 3 Security Flow
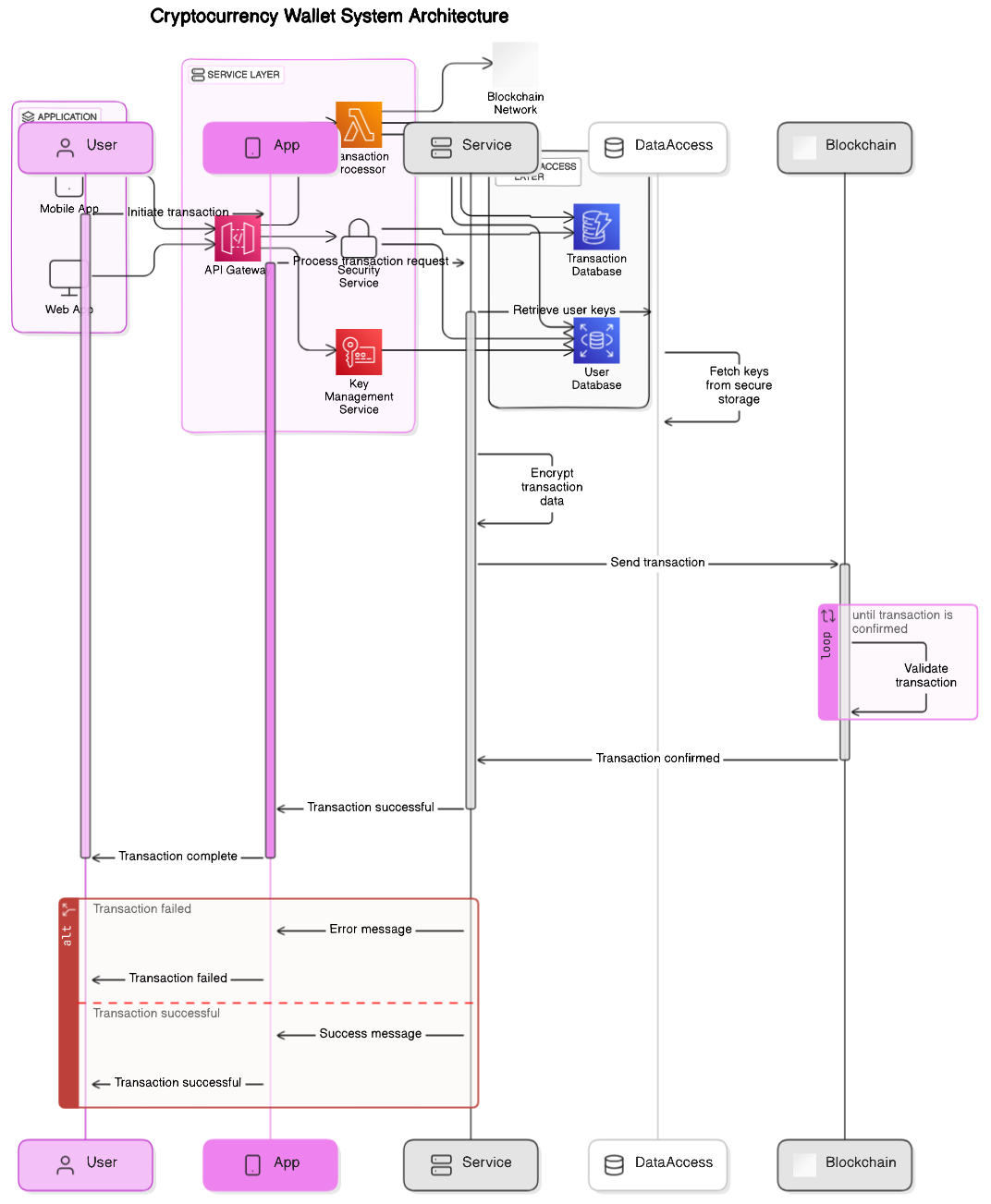
Layer 3 Security Flow Diagram
Visual representation of security protocols and data flow in Layer 3
Implementation Insights
Hybrid Hot-Cold Integration
Many architectures use a "warm" bridge where cold-stored keys are temporarily activated via MPC, avoiding full exposure. For example, during transfers, only shards of keys are used online.
Emerging Trends in 2025
Incorporation of AI for behavioral biometrics and formal verification of smart contracts to automate threat detection. Providers like Fireblocks emphasize policy engines that dynamically adjust based on risk.
Best Practices
Limit funds in warm wallets (e.g., 10-20% of holdings), regularly update software, and conduct audits. For developers, focus on secure coding and black-box testing.
This layered approach significantly reduces vulnerabilities, but users should tailor it to their risk profile—e.g., high-value holders might add physical security measures like safes for hardware components.
References
Token Metrics. (2025). How to Store Cryptocurrency Safely in 2025 | Hot vs Cold Wallets.
tokenmetrics.comLeewayHertz. (2025). Hot and Cold Wallet Architecture.
leewayhertz.comResearchGate. (2024). Multilayered Defense-in-Depth Architecture for Cryptocurrency Wallet.
researchgate.netCoincover. (2025). Developing resilient crypto wallets: security best practices.
coincover.comChainGPT. (2025). Your Crypto Wallet Guide For 2025.
chaingpt.orgCoincub. (2025). Top Hot & Cold Wallets for Secure Crypto Storage.
coincub.comCobo. (2025). Cold Wallet vs Hot Wallet: Key Differences Explained (2025 Guide).
cobo.comOneKey. (2025). Best CRYPTO.ORG Wallets in 2025.
onekey.soECCU. (2024). A Cybersecurity Guide to Safely Storing Your Cryptocurrency.
eccu.eduDeFi Planet. (2024). How Fireblocks' Multi-Layered Security Prevents the Worst Crypto Attacks.
defi-planet.comHacken. (2024). Wallet Security: Best Practices For Keeping Your Crypto Safe.
hacken.ioZimperium. (2024). Crypto Wallet Security | Mobile Security Glossary.
zimperium.comStellar Cyber. (2024). Advanced Techniques to Secure Your Crypto Wallet Safely.
stellarcyber.aiQuickNode. (2024). An Introduction to Crypto Wallets and How to Keep Them Secure.
quicknode.comRapid Innovation. (2024). Ultimate Crypto Wallet Security Guide 2024: Protect Your Digital Assets Now.
rapidinnovation.ioApriorit. (2024). Crypto Wallet Security Best Practices.
apriorit.comTrakx. (2024). Crypto Security: Best Practices To Protect Digital Assets.
trakx.ioAssam Tribune. (2024). How to Keep Your Crypto Safe: Wallets, Exchanges, and Best Practices.
assamtribune.com